If you have been following this blog you have most likely encountered a few blog posts related to SAP integration. I also wrote two chapters related to SAP integration in a BizTalk book last year. In all of the journeys that I have taken with SAP, not once have I encountered a situation were I needed to receive a request from SAP that required a synchronous response. All of my previous experience required asynchronous messaging with SAP when receiving data from SAP. We now have a scenario that requires SAP to send BizTalk a “fetch” request and BizTalk needs to provide this information in near real-time. What was very interesting about this scenario many people within our organization didn’t think, or know it was possible. I guess it was tough for some to wrap their head around the concept of SAP actually needing information from another system since it tends to be a System of Record.
SAPRFC.INI HUH???
A good starting point for this scenario is in the MSDN documentation. Initially I thought it would be pretty straight forward and would resemble a situation where BizTalk receives an IDOC. That was until I received an error similar to the one below indicating that an saprfc.ini file could not be found when enabling the SAP Receive Location.
Log Name: Application
Source: BizTalk Server
Date: 3/6/2012 7:12:53 PM
Event ID: 5644
Task Category: BizTalk Server
Level: Error
Keywords: Classic
User: N/A
Computer: SERVER
Description:
The Messaging Engine failed to add a receive location "Receive Location2" with URL "sap://CLIENT=010;LANG=EN;@a/SAPSERVER/00?ListenerDest=ZRFCADD&ListenerGwServ=sapgw00&ListenerGwHost=SAPHOST&ListenerProgramId=Biztalk_Z_Add&RfcSdkTrace=False&AbapDebug=False" to the adapter "WCF-SAP". Reason: "Microsoft.Adapters.SAP.RFCException: Details: ErrorCode=RFC_OK. ErrorGroup=RFC_ERROR_SYSTEM_FAILURE. SapErrorMessage=Open file 'C:\SAPINI\saprfc.ini' failed: 'No such file or directory'. AdapterErrorMessage=Error accepting incoming connection. RfcAccept returned RFC_HANDLE_NULL..
This really confused me since I could successfully connect to SAP and receive IDOCs. After some digging, I discovered the following webpage that indicated: “The RFC library will read the saprfc.ini file to find out the connection type and all RFC-specific parameters needed to connect to an SAP system, or to register an RFC server program at an SAP gateway and wait for RFC calls from any SAP system.”
So how do we solve this?
- The first thing that we need to do is to create a System Variable called RFC_INI. We then need to provide a path and a filename. For the purpose of my example I used C:\SAPINI\saprfc.ini.
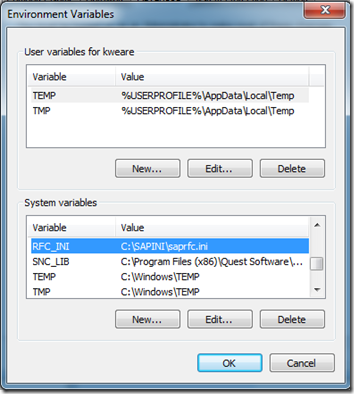
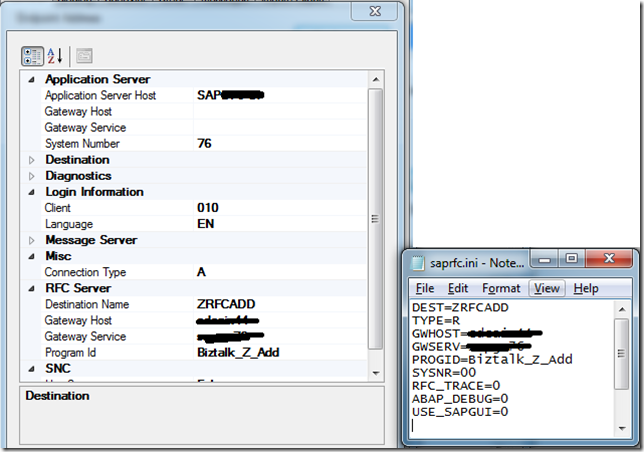
- Next we need to add the contents to our saprfc.ini file. The values that I needed to provide include:
| Field name | Value | |
| DEST | ZRFCADD | In this case, this is the name of the RFC Destination that our BASIS team created for us from SM59. More details here. |
| TYPE | R | Type R is for RFC server programs or for a client program working with another external program as RFC server program which is already registered at an SAP gateway. |
| GWHOST | SAP_HOST_NAME | In my case, this is the name of the physical server that his hosting the SAP Gateway. |
| GWSERVER | SAP_GATEWAY_NAME | The name of the SAP Gateway. A standard naming convention is: SAPGW## where ## is the system number for the SAP instance that you are working on. |
| PROGID | Biztalk_Z_Add | This is the name of the Program ID that has also been provided by BASIS. |
So if we compare the details between our Receive Location and our saprfc.ini we will see symmetry between the two. However, the values in the ini file take precedence.
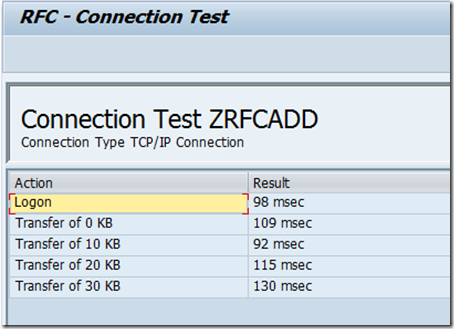
- Now that we have have our SAPRFC.ini file and SAP Receive location in order we can run a connected client test using SM59. To perform this test, launch the SM59 transaction and then expand the TCP/IP Connections node.
- Scroll through the list to find your RFC Destination. In my case, I am looking for ZRFCADD. Double click on this value.

- Click on the Connection Test button to execute the test.
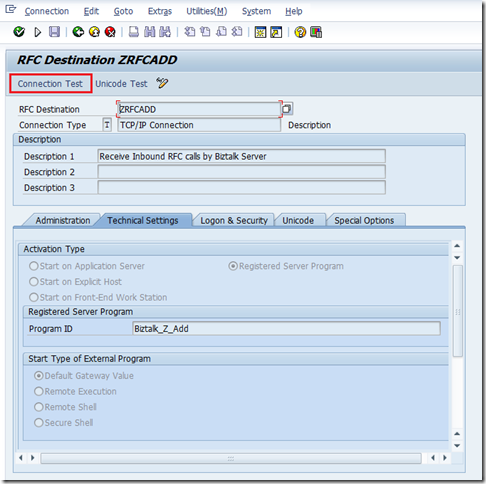
- You should see a successful Connection Test. If not, there is no point trying to call your RFC from SAP until you get this connection issue resolved. If SAP can’t perform this “ping test” it won’t be able to actually send you data. To troubleshoot this you will need to ensure that the values that you have in your receive location/ini file match the values that are defined in SM59. In most cases you will need to rely upon your BASIS Buddy to help you out. As I mentioned in my book, I do have a good BASIS buddy so this troubleshooting usually goes smoothly.
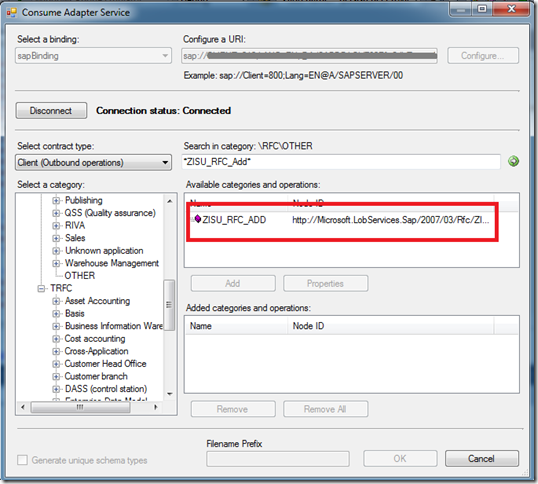
- With our connectivity issues out of the way, we can browse for our desired schemas using the BizTalk Consume Adapter Service Wizard and then add them to our solution.
- We can now build out the rest of our application. In my case I have a very simple map that will add two values that occur in the request message and provide the sum in the response message.
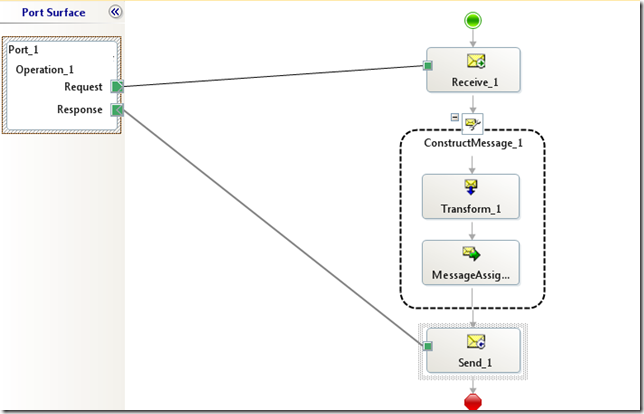
- The only special consideration that we need to take care of is to set the WCF.Action in the Response message. We can do this inside a Message Assignment shape. If you don’t take care of this, you will receive a run time error.
sapResponse(WCF.Action) = "http://Microsoft.LobServices.Sap/2007/03/Rfc/ZISU_RFC_ADD/response";
We now are in a position to deploy our application and start receiving requests from SAP.
Conclusion
Overall the process was pretty similar to receiving IDOCs with the exception of the INI file and the WCF Action property requiring being populated. Performance is similar to receiving or sending IDOCs so you won’t take any additional performance hits.












